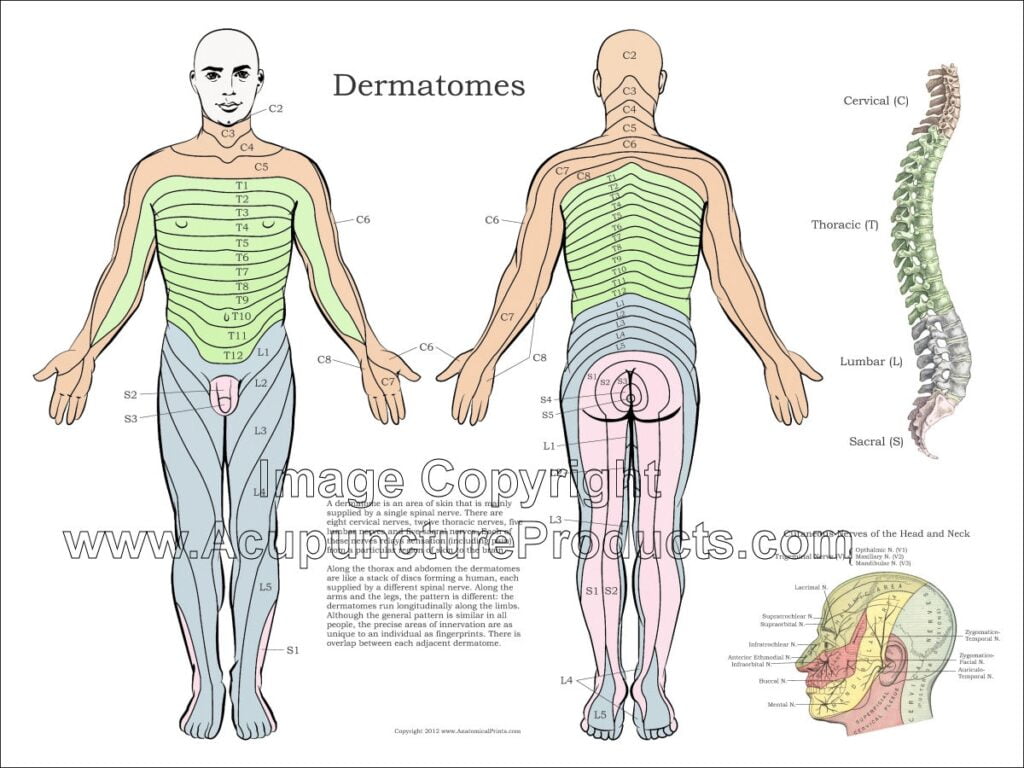
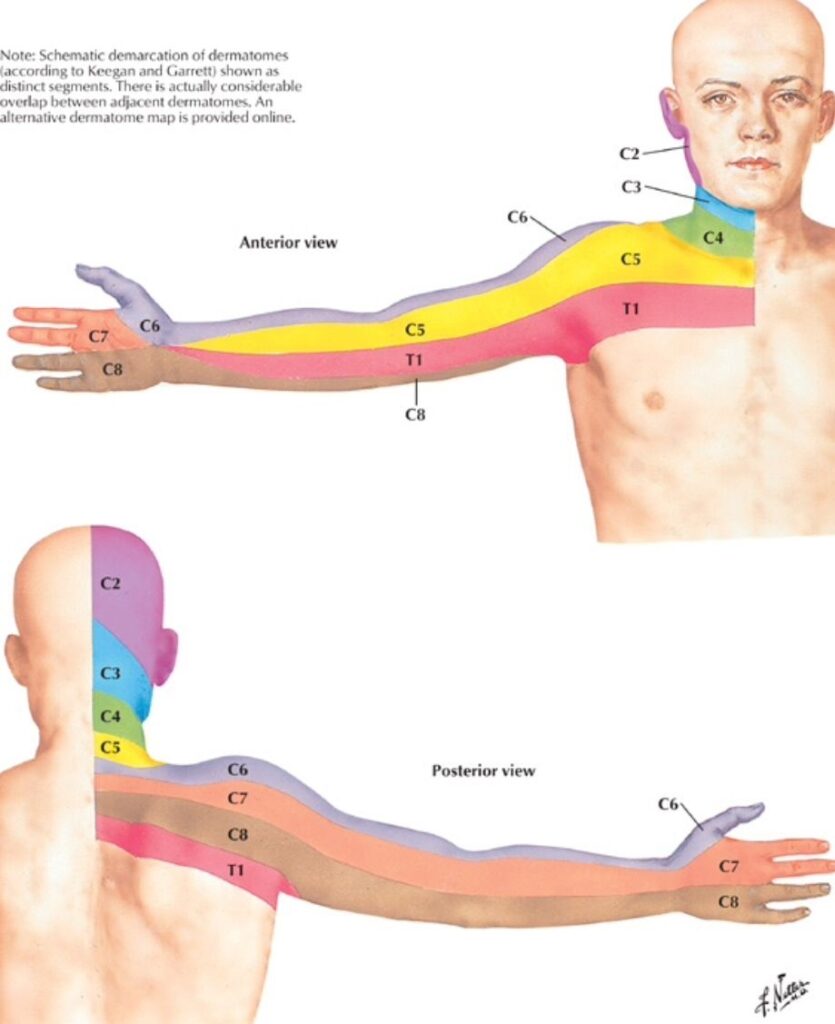
C7 Dermatomal Pattern – A dermatome is the area of the skin of the human anatomy that is generally provided by branches of a single spine sensory nerve root. These spine sensory nerves go into the nerve root at the spinal cord, and their branches reach to the periphery of the body. The sensory nerves in the periphery of the body are a kind of nerve that transmits signals from experiences (for instance, pain symptoms, touch, temperature) to the spine from particular locations of our anatomy.
Why Are Dermatomes Necessary?
To understand dermatomes, it is necessary to understand the anatomy of the spinal column. The spinal column is divided into 31 sections, each with a pair (right and left) of posterior and anterior nerve roots. The types of nerves in the anterior and posterior roots are various. Anterior nerve roots are responsible for motor signals to the body, and posterior nerve roots get sensory signals like discomfort or other sensory signs. The anterior and posterior nerve roots integrate on each side to form the back nerves as they leave the vertebral canal (the bones of the spinal column, or foundation).
Dermatomes Of The Body Poster
Dermatomes Of The Body Poster
Dermatome diagrams
Dermatome maps depict the sensory circulation of each dermatome throughout the body. Clinicians can evaluate cutaneous experience with a dermatome map as a method to localise sores within central worried tissue, injury to specific spine nerves, and to figure out the degree of the injury. Numerous dermatome maps have been established throughout the years however are often contrasting. The most typically used dermatome maps in significant textbooks are the Keegan and Garrett map (1948) which leans towards a developmental analysis of this concept, and the Foerster map (1933) which associates better with clinical practice. This article will review the dermatomes using both maps, recognizing and comparing the major differences in between them.
It’s necessary to stress that the existing C7 Dermatomal Pattern are at finest an evaluation of the segmental innervation of the skin considering that the many areas of skin are generally innervated by at least 2 spine nerves. For instance, if a patient is experiencing numbness in only one location, it is unlikely that numbness would take place if only one posterior root is impacted because of the overlapping division of dermatomes. At least 2 surrounding posterior roots would require to be affected for tingling to take place.
Cervical Radiculopathy Spine Orthobullets
Cervical Radiculopathy Spine Orthobullets
The C7 Dermatomal Pattern frequently play an essential function in figuring out where the damage is coming from, providing physicians a hint as to where to look for signs of infection, swelling, or injury. Common illness that might be partly recognized through the dermatome chart include:
- Spinal injury (from a fall, etc.)
- Compression of the spinal cord
- Pressure from a tumor
- A hematoma (pooling blood)
- Slipped or bulging discs
A series of other analysis methods and signs are necessary for identifying injuries and diseases of the spine, including paralysis, bladder dysfunction, and gait disturbance, in addition to analysis processes such as imaging (MRI, CT, X-rays checking for bone damage) and blood tests (to look for infection).
Dermatomes play an important function in our understanding of the human body and can help patients better comprehend how problem to their back can be recognized through different signs of pain and other strange or out-of-place sensations.C7 Dermatomal Pattern
When the spine is harmed, treatments often include medication and intervention to minimize and combat swelling and exercise, inflammation and rest to minimize pain and strengthen the surrounding muscles, and in specific cases, surgical treatment to eliminate bone stimulates or fragments, or decompress a nerve root/the spine.C7 Dermatomal Pattern